Background
- Retrace Q function은 off-policy return based Q estimation algorithm인데, data efficiency도 좋고, convergence가 보장되어 있다.
-
TD-error 를 계산한다.
-
error를 따라서 learning rate 에 맞게 업데이트한다.
하지만 rollout(trajectory)가 off policy라면, importance sampling을 해야한다.
importance sampling의 importance weights은 high variance를 불러올 수 있기 때문에, 큰 위험이 되지만, Retrace Q-value estimation은 Q update 량을 constant c 에 대해
\[min(c, \frac{\pi(A_{\tau}|S_{\tau})} {\beta(A_{\tau}|S_{\tau})})\]로 제한한다. ACER는 \(Q^{ret}\) 를 사용해서 \(Q\) 와 L2 loss로 estimation한다.
Abstract
experience replay를 가진 actor-critic algorithm을 제시한다. 또한, bias가 보완된 truncated importance sampling과, stochastic dueling network architecture, TRPO method를 사용하는데 뒤에서 자세히 설명하겠다.
1. Introduction
현실적인 시뮬레이션 환경은 최근에 돌파구로 뜨고있다. 좀더 현실적인 환경에선 agent는 더 진보된 성능을 보인다. 하지만 이러한 장점은 시뮬레이션에 대한 cost의 증가를 내포하고 있다. 특히 단위 시간 단위에서 심할 것이고, 이를 줄이기 위해, 시뮬레이션 스텝을 줄여야 한다. 그렇기 때문에 sample efficiency가 현실에서 RL을 쓰기 위해 높아야한다.
Experience replay는 Q-learning에서 유명세를 얻었는데, 주 목적은 sample correlation을 줄이기 위해서 였다. 이 replay buffer는 사실 sample efficiency를 높이기 위한 중요한 도구이고, 여기서 비교 대상으로 사용한 DQN을 보자면, 두가지 중요한 단점이 존재한다. 첫째로, deterministic한 환경에서로 domain이 제한된다. 둘째로, large action space에서 Q function에 따라 greedy action을 찾는 것은 cost가 너무 크다.
PG는 AI와 Robotics에서의 큰 진전을 이루는데 많은 역할을 했다. 하지만 많은 알고리즘들이 Continuous domain에 제한되었고, 이 둘에 함께 applicate할 수 있는 알고리즘 A3C는 sample inefficient하다.
continuous와 discrete action space에서 모두 적용되는 method는 그동안 RL에서 오랫동안의 허들이었다. 하지만 이 ACER가 첫번째로 잘 해결한 논문이라고 설명한다.
2. Background And Problem setup
discrete action env 는 Section 3,4 에서, continuous action env는 Section 5 에서 다룬다.
\[g = \mathbb{E}_{x_{0:\infty},a_{0:\infty}}[\sum_{t \geq 0}{A^{\pi}(s_t,a_t)\nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)}}](1)\]같은 기본적인 PG update notation을 가져왔는데,[Real-time reinforcement learning by sequential Actor-Critics and experience replay] 내용이 조금 있다. GAE 처럼 거긴 advantage function에 lambda 가 계속 곱해져, unbiased 됐지만, 여기서는 reward에만 계속 lambda가 곱해져 unbiased 된다. 여튼 estimator는 higher bias, low variance를 가지는 반면에, 여기서의 policy gradient estimator는 higher variance and low bias를 가진다. \(R_t\) 과 value function의 결합은 ACER에 숨어있는 중요한 요소이다.
이렇게 k번의 time step의 값으로 Advantage estimator를 구하면,
\[\hat{g}^{a3c} = \sum_{t \geq 0}{((\sum_{i=0}^{k-1}{\lambda ^i r_{t+i}})+ \lambda ^k V^{\pi}_{\theta_v}(x_{t_k}) - V^{\pi}_{\theta_v}(x_t)) \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)}}(2)\]다음과 같은 식을 얻는다. 참고로, \(\theta\) 는 policy, \(\theta_v\) 는 value network이다.
3. Discrete Actor Critic with Experience Replay
off policy learning에서 experience replay를 도입하는 것은 sample effciency를 높이는 당연한 전략이다. 하지만, variance를 관리하고 stability를 유지하는 것은 상당히 어려운 일이다. 그래서 이를 위해 가장 흔한 접근으로, Importance sampling을 도입했다.
\[\hat{g}^{imp} = (\prod_{t=0}^k \rho_t) \sum^k_{t=0}(\sum^k_{i=0}{\lambda^i r_{t+i} }) \nabla _{\theta} \log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)}\]여기서 \(\rho_t = \frac {\pi (a_t|x_t)} {\mu (a_t|x_t)}\) 인데, \(\mu\) 는 당연히, 이전의 policy이다. 이렇게 구하게 되면, unbiased 됐지만, high variance를 겪는데, 이는, bounded importance weights 이 아니기 때문에 큰 variance를 갖기 때문이다. 이러한 importance weights의 exploding 을 막기 위해선, truncated importance sampling을 하게 되는데, 이 값은 variance를 bound하지만, 또, significant bias가 생기게 된다.
이를 distribution을 제한하면서 marginal value function을 사용해 이 문제를 해결 했는데, gradient에 관한 근사식은 다음과 같다.
\[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t \sim \beta,a_t \sim \mu}[\rho_t \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)}Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)] (4)\]이 (4)에서 주목할 점은 첫째로, \(Q^{\mu}\) 를 사용한다는 점이다. 둘째로, importance sampling weights를 사용하는게 아닌, marginal importance weight \(\rho_t\)를 사용한다. 그렇기 때문에, lower variance를 가진다. 그리고 (4)에서 \(Q^{\pi}\) 를
\[R^{\lambda}_t = r_t + (1 - \lambda) \gamma V(x_{t+1}) + \lambda \gamma \rho_{t+1}R^{\lambda}_{t+1}\]로 구한다. 이번 subsection에서는 \(Q^{\pi}\) 를 구하기 위해, [Safe and efficient off-policy reinforcementlearning] 에 나온 방법을 사용하는데, importance weight truncation technique를 stability를 향상 시킨다.
3.1 Multi-Step Estimation of the State-Action Value Function
이 논문에서는 \(Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)\) 를 Retrace([Safe and efficient off-policy reinforcementlearning]에 나옴) 방법을 통해 업데이트하는데, 수식은 다음과 같다.
\[Q^{ret}(x_t,a_t) = r_t + \gamma \overline{\rho}_{t+1}[Q^{ret}(x_{t+1},a_{t+1}) - Q(x_{t+1},a_{t+1})] + \gamma V(x_{t+1}) (5)\]여기서 \(\overline{\rho}\) 는 truncated importance weight 이고, \(\overline{\rho} = min \{c, \rho_t \}\) 이다. Retrace 를 사용하는 이유는 off policy인데, low variance를 가지고 tabular 환경에서 converge하는 것이 증명되었기 때문이다.
recursive retrace equation은 추정된 Q 값에 의존하는데, 여기서는 CNN을 사용해 action-value function과 action을 같이 추정한다. value function을 안쓰는 이유는 Q를 통해 쉽게 추정가능하기 때문이다.
critic은 \(Q^{ret}(x_t,a_t)\) 와의 mse를 통해 update한다. 이는 Retrace가 critic을 빠르게 배우는것을 가능하게 하기 때문이다. 그러므로, \(Q^{ret}\) 의 역할은 두가지이다. bias를 줄이고, faster learning을 하게한다.
3.2 Importance weight truncation with bias correction
\[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t a_t}[\rho_t \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]\]의 식을 보고, 왜 marginal하게 나눴을 때, 이렇게 되는지 이해가 잘 안갔을 것이다.
\[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[\overline{\rho} \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}] + [\mathbb{E}_{a \sim \pi}[\sum{[\frac {\rho_t - c} {\rho_t}]_{+} \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}}]](7)\](7)을 유도하기 전에 \(\rho \leq c\) 이라면, 첫번째 term만 존재하기 때문에, 그대로 구하면 된다. 하지만, \(\rho \geq c\) 라면, 다음과 같이 유도할 수 있다.
\[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[\rho_t \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]]\] \[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[(\rho_t -c + c)\nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]]\] \[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[c \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]] + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[ (\rho_t - c) \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]]\] \[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[c \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]] + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\sum_{a \in A}{(\rho_t - c) \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}}]\] \[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[c \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]] + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\sum_{a \in A}{\mu(a_t|x_t) (\rho_t - c) \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}}]\] \[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[[c \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]]] + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\sum_{a \in A}{\frac {\pi(a_t|x_t)} {\pi(a_t|x_t)} \mu(a_t|x_t) (\rho_t - c) \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}}]\] \[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[c \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]] + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\sum_{a \in A}{\frac {\mu(a_t|x_t)} {\pi(a_t|x_t)} \pi(a_t|x_t) (\rho_t - c) \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}}]\] \[g^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[c \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}] + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a \sim \pi}[\frac {\rho_t - c} {\rho_t} \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{\pi}(x_t,a_t)}]]\]이므로 (7)과 같다. 두번째 term을 correction term이라고 여기서는 부르는데, c를 아주 크게 잡았을 때, variance가 아주 클때만 이 두번째 term이 activate 됐다. 거기다가, 아무리 \(\rho\) 값이 커져도 이 term이 1에 수렴하기 때문에, 첫째항의 update도 제한되고, 두번째 term도 \([ \cdot ]\)이 1로 수렴하기 때문에 variance가 줄어든다. 하지만 unbiased됐다는 것에 주목해야 한다.
\[\hat{g}^{marg} = \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a_t}[\overline{\rho_t} \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q^{ret}(x_t,a_t)}] + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a \sim \pi}[\sum{\frac {\rho_t - c} {\rho_t} \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)Q_{\theta_v}(x_t,a_t)}}]] (8)\](8)를 보면, \(\mu (a_t|x_t)\) 를 따른 Expectation 값은 \(Q^{ret}\) 를 따르고, 새로운 policy를 따르는 Expectation은 \(Q_{\theta_v}\) 를 따른다. 이는 \(Q^{ret}\)를 두번째 term에서 추정할 수 없기 때문이다.
그리고 variance를 줄이기 위해 Advantage-function을 쓰는 모습도 보여주고, 여기서 \(c = \infty\) 로 가면, 완전히 Retrace를 사용하는 off policy gradient를 하고, \(c= 0\) 로가면, 그냥 actor-critic이 된다.
그리고, (8)의 첫번째 term의 기댓값은 이미 behavior policy \(\mu\) 로 인해 approximate 됐기 때문에 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있따.
\[\hat{g}^{acer} = \overline{\rho_t} \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)[Q^{ret}(x_t,a_t)-V_{\theta_v}(x_t)]} + \mathbb{E}_{x_t}[\mathbb{E}_{a \sim \pi}[\sum{\frac {\rho_t - c} {\rho_t} \nabla_{\theta}\log{\pi_{\theta}(a_t|x_t)(Q_{\theta_v}(x_t,a_t) - V_{\theta_v}(x_t)}}]] (9)\]continuous control domain에서도 (9)는 Stochastic value gradient를 일반화할 수 있다. c = 0 이고, reparameterization trick이 사용된다면!
3.3 Efficient trust Region Policy Optimization
actor-critic은 자주 high variance를 보이므로, 안정성을 높이기 위해서는 step마다의 변화를 어느정도 제한해야할 의무가 있다. 하지만 그저 적은 learning rate는 충분하지않다. 그래서 TRPO를 사용하기로 했다.
그러나 TRPO는 계산마다 Fisher-vector 를 곱하는 계산을 계속해야하므로, 여기서는 average policy network를 유지하면서, 너무 기존과 멀어지지않도록 한다.
policy network를 두 파트로 나누는데, \(\phi_{\theta}(x)\)로 statistics를 만들고, distribution f에의해 policy가 확실하게 정해진다.
average policy network를 \(\phi_{\theta_a}\) 로 나타내는데, 이 \(\theta_a\)를 soft update를 하게 된다.
\[\hat{g}^{acer} = \overline{\rho_t} \nabla_{\phi_{\theta}(x_t)}\log{f(a_t|\phi_{\theta}(x))[Q^{ret}(x_t,a_t)-V_{\theta_v}(x_t)]} + \mathbb{E}_{a \sim \pi}([\frac {\rho_t - c} {\rho_t}]_+ \nabla_{\theta}\log{f(a_t|\phi_{\theta})(Q_{\theta_v}(x_t,a_t) - V_{\theta_v}(x_t)}) (10)\]을 보면, randomize하게 action 뽑는 f 부분은 빼고 gradient를 구하는 디테일을 보인다.(나 위에 수식 Latex 많이 틀렸는데 언제고치는지 ㅠㅠ)
average policy network를 이용해 여기서는 trust region update를 두 state로 나눈다. 첫번째로, 다음과 같은 linearized KL divergence constraint를 가진 optimization problem를 푸는데,
\[minimize_{z} \frac{1}{2}||\hat{g}_t^{acer} - z ||^2\] \[subject to \nabla_{\phi_{\theta}(x_t)}D_{KL}[f(\cdot|\phi_{\theta_a}(x_t))||f(\cdot|\phi_{\theta}(x_t))]^T z \leq \delta\]여기서, constraint가 linear하기 때문에, 구하기도 쉽고, solution은 쿤커터 조건을 사용하면 쉽게 풀리는데 다음과 같다.
\[z^* = \hat{g}_t^{acer} - max\{0, \frac{k^T\hat{g}_t^{acer}-\delta}{||k||^2_2}\}k\] \[k = \nabla_{\phi_{\theta}(x_t)}D_{KL}[f(\cdot|\phi_{\theta_a}(x_t))||f(\cdot|\phi_{\theta}(x_t))]\]이 gradient 를 구하는 form은 자연스러운데, 만약 제약조건이 충족되면, \(\phi_{\theta}(x_t)\) 에 대한 gradient는 변화가 없을 것이다. 충족되지 않으면, k 방향에 대한 update크기가 줄어들게 되어 효과적으로 current policy와 average policy 를 조금 바꾸어 업데이트 할 것이다.
다음으로, back-propagation에서도 장점을 갖는데, 특히 \(\phi_{\theta}\) 이다. policy network는 다음과 같이 업데이트 된다.
\[\frac {\partial \phi_{\theta}(x)}{\partial \theta} z^*\]4. Result on Atari
여기선 실험에 쓰이게 된 hyperparameter와 network architecture등에 대해 많은 얘기를 한다. 구현할 때 좀 더 꼼꼼히 참고할 예정이다.
5. Continuous Actor-Critic with Experience Replay
Retrace는 Q와 V가 모두 필요한데, 여기서는 Q만 사용해 V를 유도한다. 이 section에서는, trust region update와 함께, 새로운 해결법을 제시한다.
5.1 Policy Evaluation
Retrace는 \(Q_{\theta_v}\) 를 제공해주나 \(V_{\theta_v}\) 는 제공하지 않는다. 그래서 여기서는 주어진 \(Q_{\theta_v}\)를 importance sampling을 통해 \(V_{\theta_v}\) 를 구하나, 높은 variance를 가지게 된다.
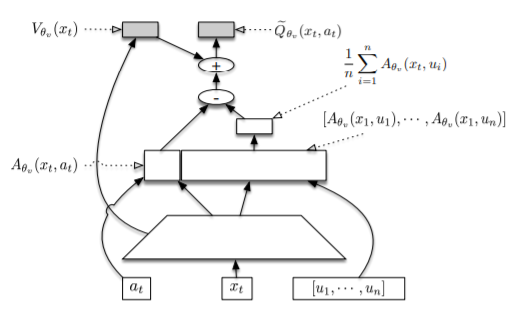
여기서는 Stochastic Dueling Network(SDN)라는 새로운 architecture 구조를 제안하는데, \(V^{\pi}\) 와 \(Q^{\pi}\) 를 둘다 계산하기 위해, 디자인되었다. SDN은 각 스텝마다 stochastic estimation \(\tilde{Q}_{\theta_v}\) 를, deterministic estimation \(V_{\theta_v}\) 를 주게 된다.
\[\hat{Q}_{\theta_v} (x_t,a_t) \sim V_{\theta_v}(x_t) + A_{\theta_v}(x_t,a_t) - \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^n{A_{\theta_v}(x_t,u_i)}, u_i \sim \pi_{\theta}(\cdot | x_t) (13)\](13)식은 \(\pi_{\theta}(\cdot|x_t)\) 에 의해 sampling된, \(E_{a \sim \pi(\cdot | x_t)} [V^{\pi}(x_t,a)]\) 로 볼 수있는 세번째 term을 뺌으로써, distribution f 의
(13)식은 Dueling-DQN의 아이디어에서 나왔는데, Dueling-DQN에서는 Q를 A와 V의 mixed network에서 구하는데, 좋은 Q라고 좋은 A와 V를 보장할 수 없기 때문에, A에서 max값을 뺐더니 identifiability가 보장됐고, off-policy로 바뀌는 대신 mean값으로 빼게되면 stability가 좋아졌다는 점에서 (13)의 식이 나왔다.
V를 update할때, \(\tilde{Q}_{\theta_v}\) 가 사용 되기 때문에, 오류가 같이 전파된다.(t 까지의 n step 고려해 expectation 을 하기 때문이다.)
추가적으로 SDN에서는 \(V^{\pi}\) 를 구할 때, 새로운 방법을 사용하는데, 앞처럼 clipping을 하는 기법을 사용한다.
\[V^{target}(x_t) = min \{ 1, \frac{\pi(a_t|x_t)}{\mu(a_t|x_t)} \} (Q^{ret}(x_t,a_t) - Q_{\theta_v}(x_t,a_t)) + V_{\theta_v}(x_t) (14)\]마지막으로, continuous domain 에서 \(Q^{ret}\)을 estimating 할때는, importance weights 를 다음과 같이 해서 구했다.
\[\overline{\rho}_t = min \{ 1, \left( \frac {\pi(a_t|x_t)}{\mu(a_t|x_t)}\right)^{\frac {1}{d}} \}\]d는 action dimension이고, 이렇게해야 converge가 빨랐다.
5.2 Trust Region Updating
continuous control domain에 trust region updating을 적용하기 위해서, 먼저 distribuion f를 정하고, gradient specification \(\hat{g}_t^{acer}\) 를 적당하게 바꿔야한다. 여기서는 f를 diagonal covariance를 고정 시키고 mean \(\phi_{\theta}(x)\)를 사용하는, gaussian distribution 를 이용했다.
\[\hat{g}^{acer} = \overline{\rho_t} \nabla_{\phi_{\theta}(x_t)}\log{f(a_t|\phi_{\theta}(x))[Q^{opc}(x_t,a_t)-V_{\theta_v}(x_t)]} + ([\frac {\rho_t(a_t') - c} {\rho_t(a_t')}]_+ (\tilde{Q}_{\theta_v}(x_t,a_t') - V_{\theta_v(x_t)})\nabla_{\phi_{\theta}(x_t)}\log{f(a_t'|\phi_{\theta})} (16)\]\(Q^{opc}\)는 importance ratio가 1로 변형된 \(Q^{ret}\)이다.
6,7 section
여긴 retrace에대한 좀더 자세한 설명도 있고, conclusion이 있다. 자세한 설명은 생략!
Reference
- http://www.secmem.org/blog/2019/06/17/ACER/
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.01224.pdf
- https://lilianweng.github.io/lil-log/2018/04/08/policy-gradient-algorithms.html